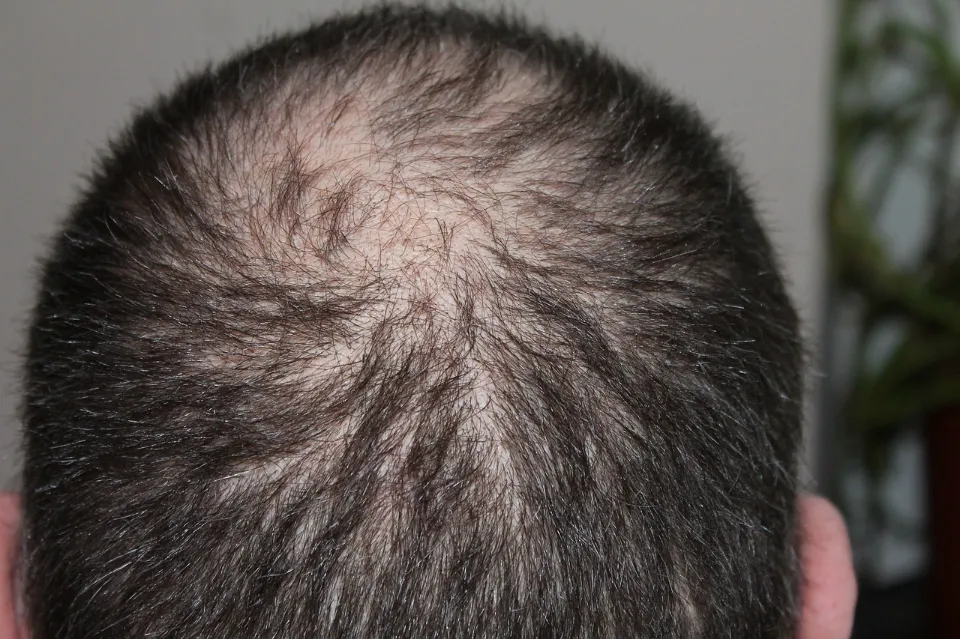
Do you have a late 40s or early 50s age range? Testosterone levels that fluctuate may be the cause of your hair loss. Wondering what that is?
Both men and women have testosterone, which is a hormone involved in male sex. It serves a variety of functions, including the growth of particular secondary sexual traits in men. Hair loss is a known side effect of this hormone, whether it is present in very low or high levels.
Although fluctuating testosterone levels can lead to balding in both men and women, testosterone itself does not directly cause hair loss.
Let’s examine the true causes of and effective management strategies for testosterone hair loss.
What Are the Types of Testosterone?

A lot of researchers concluded that testosterone in high levels can result in hair loss due to a specific hormone that it produces. The human body can produce testosterone in the following ways.
1. Free Testosterone
There are no proteins in your body that are linked to this form. Free testosterone is a hormone that binds to testosterone receptors and is taken up by cells to perform some tasks.
2. Dht
Testosterone is the source of dihydrotestosterone. It is produced by the enzyme 5-alpha reductase and DHEA, which is more prevalent in women (1). Skin, hair, and the prostate contain this hormone. It attaches to hair follicles and shrinks them, causing your hair to thin out and eventually fall out (2).
Men develop secondary sexual characteristics primarily as a result of testosterone and DHT. These include:
- A change in voice
- Increased hair on the body
- Sperm production
- Growth of the testicles
High Testosterone Vs Low Testosterone
Hair on your body grows through follicles. A hair strand is contained in a follicle, which is a tiny pore under your skin. Your hair grows in a cycle that lasts between two and five years, after which it enters a resting phase and falls out.
Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) is a hormone that is produced in the body when there are high levels of androgens. DHT binds to certain proteins in the body, which in turn reduces the size of your hair follicles. This may result in thinning of the hair and may even delay the growth of new hair strands.
Hair loss can be brought on by both low and high testosterone levels. We need to be aware that people with low testosterone levels might actually have the same amount of DHT that causes hair loss. It has been shown that men with male pattern baldness have low testosterone levels with average DHT levels in their body. Some people have the same amount of DHT as others, but their hair follicles are genetically programmed to be more sensitive to DHT. That Your Hair Loss Is Caused By Varying Testosterone Levels? This increases their follicles’ susceptibility to shrinking in size.
Androgenetic alopecia in men and women is linked to fluctuating testosterone levels and genetics. It happens in a particular pattern that could eventually lead to total baldness.
1. Male Pattern Baldness
It starts from the temples, eventually resulting in complete balding. Frontal baldness is the beginning of androgenetic alopecia for men.
2. Female Pattern Baldness
The part-line is typically where hair thinning starts. It may or may not result in complete balding. Female pattern baldness affects PCOS sufferers as well as people who are 40 to 50 years post-menopause.

What Causes Hair Loss
Before we go into detail about testosterone and your hair, it’s important to briefly clear up what exactly male hair loss is, as well as the key factors that cause it to occur.
You may lose hair as a man for a number of different reasons. Infections, illnesses that cause fever, stress, problems with your diet, and the use of specific kinds of medications, such as chemotherapy drugs used in cancer treatment, are some of these.
Even some hairstyles can make you lose hair because they pull on your hair follicles, which is known as traction alopecia.
The majority of these conditions, like telogen effluvium, result in temporary hair loss. Once the underlying problem has been resolved, you can typically regrow your hair when a dietary issue or stressful work environment causes damage.
Male pattern baldness, also known as androgenetic alopecia, is, however, the most typical type of hair loss in men.
In contrast to most types of hair loss, which result in transient shedding, male pattern baldness results in permanent hair loss. Before resulting in a general loss of hair density, it typically starts out with a receding hairline or bald patch around your crown (the top of your head).
Male pattern baldness is a widespread condition that can affect adult men of all ages. When determining the extent of this type of hair loss, specialists use tools like the Norwood Scale, which can range greatly in severity from mild to extensive.
So what factors contribute to male pattern baldness, and how does testosterone function? Dihydrotestosterone (DHT), an androgen hormone (also known as a male sex hormone), is one of the causes of male pattern baldness. It has both genetic and androgen-related effects.
DHT can bind to receptors distributed throughout your scalp and shrink your hair follicles over time if you are genetically predisposed to pattern hair loss. This will alter your hair growth cycle.
This process is referred to as follicular miniaturization, and it can eventually lead to hair follicles that are no longer capable of producing new hairs.
As you’ve likely noticed, the word “dihydrotestosterone” is similar to “testosterone.” Not by chance, this occurs. As a byproduct of DHT, your body creates dihydrotestosterone thanks to the actions of an enzyme called 5 alpha-reductase.
5 alpha-reductase converts a tiny percentage of your testosterone into DHT can be found in some types of tissue, especially in the prostate, testicles, and skin.
This DHT plays a crucial role in the development of your prostate, genitalia, and secondary male sex traits like voice and body hair during your adolescence.
DHT doesn’t, however, have a significant physiological impact on you as an adult. On the other hand, it can lead to a number of medical problems, such as hair loss and prostate enlargement.
Numerous remedies for male pattern hair loss, including the oral drug finasteride and shampoos for hair loss, function by obstructing DHT, either at the hormone’s source or at the follicular level.
We’ve discussed the effects of DHT on your hair in more detail in our full guide to DHT and male hair loss.
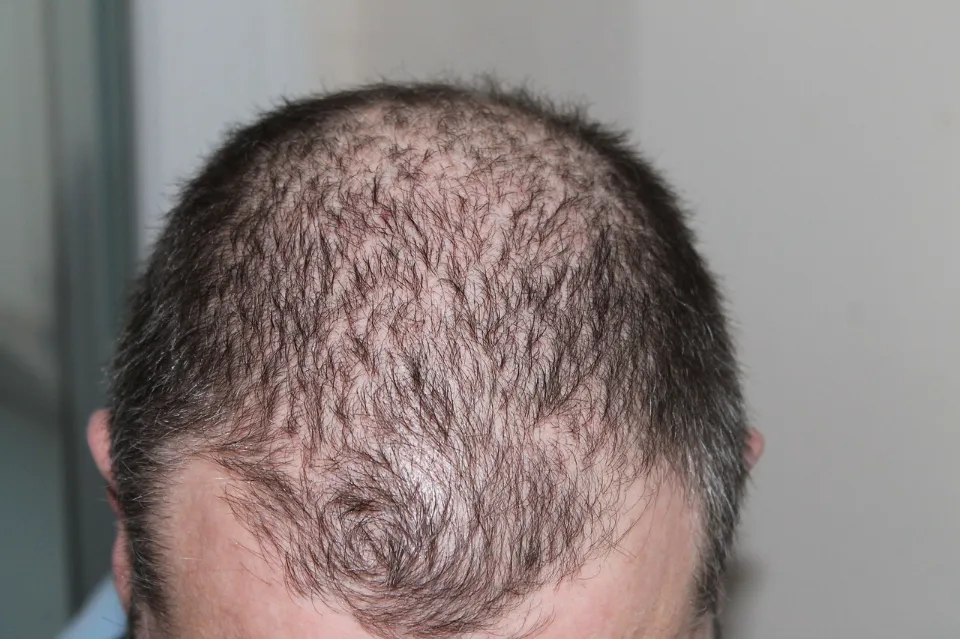
How Can You Treat Hair Loss Caused by Fluctuating Testosterone Levels?
There are a number of medications that have proved to be effective in treating hair loss caused by DHT. These medicines are divided into two categories – blockers and inhibitors.
DHT blockers are drugs that stop it from attaching to the 5 alpha reductase enzyme. DHT inhibitors can help reduce the production of the hormone.
1. Finasteride
An oral medication called finasteride has been shown to be successful in treating male pattern baldness. Studies suggest that finasteride had an 87 percent success rate in hair regrowth in men. This drug acts as a blocker by attaching to the 5 alpha reductase enzyme and preventing it from doing what the DHT hormone would otherwise do.
2. Minoxidil
A DHT blocker is minoxidil. Initially, minoxidil was a medication given to people with high blood pressure. Some of these patients started to grow their hair out too much as a side effect.
This medicine typically helps widen blood vessels to enhance blood flow. By improving blood flow to hair follicles, topical minoxidil can aid in promoting hair growth.
3. Biotin
Biotin is a Vitamin B derivative that turns nutrients into energy, which is used by your cells to carry out their functions. Keratin is a protein that makes up most of your hair and biotin also enhances its production. According to studies, biotin promotes healthy hair growth and stops hair loss.
4. Pumpkin Seed Oil
In men with male pattern baldness, studies show that using pumpkin seed oil can reduce hair loss. Pumpkin seed oil is a DHT blocker, thereby preventing hair loss and hair thinning.
5. B Vitamins
B vitamins are essential for maintaining the health of your scalp and hair. The absence of these vitamins has reportedly been linked to hair thinning and eventually hair loss. They enhance the blood flow to your hair follicles. B vitamins can stop hair loss even though they can’t necessarily restore hair growth.
Side-Effects of DHT Blockers and Inhibitors
- Erectile dysfunction
- Ejaculating too early
- Excess fat around the breast area
- Darkened hair on the face
- Rashes
- Feeling sick
- Vomiting
- Ejaculating too late
- Heart failure
Who is at Risk of Losing Hair?
Pattern baldness in both men and women is associated with hair loss brought on by varying testosterone levels.
Female pattern baldness typically affects women after menopause as their androgen levels tend to rise and their estrogen levels tend to decline. Additionally, this type of balding is frequently associated with genetics, according to researchers.

Wrapping Up
Fluctuating testosterone can result in balding in both men and women. Male and female baldness is caused by the hormone dihydrotestosterone, which is produced by testosterone.
Some people may be genetically more sensitive to this hormone than others, who may also have high levels of it. It is possible to stop hair loss by using medications that have been shown to prevent DHT from interacting with hair follicles.
FAQs
Is Testosterone the Reason I Am Balding?
Sometimes, having too much testosterone in your body can lead to hair loss and damage. It has been observed that out of all the male patients suffering from hair loss, majority have depicted hair loss due to testosterone imbalance. It can be a significant factor in hair loss, even though it is not the only one.
Does Testosterone Help Hair Growth?
Since testosterone is an androgen, it can help with hair growth. However, it causes facial and body hair to grow. Unfortunately, it doesn’t promote hair growth on our heads, which is where we most need it. In fact, having too much of it in our bodies can cause scalp hair loss.